[DIGEST: NPR, New York Times, CNN]
When the Ebola virus struck West Africa in 2014, the world was defenseless. There was no vaccine and no effective treatment. In all, the virus killed 11,000 people, with nearly 30,000 infected.
Two years later, scientists have announced in a report in The Lancet that they have developed a highly-effective vaccine against the virus.
Although still in the experimental stages, in trial the vaccine, called rVSV-ZEBOV, has been 100 percent effective in trials. Said Ira Longini, a biostatistician at the University of Florida, “It’s very unusual to have a vaccine that protects people perfectly.”
The 100 percent efficacy is likely the result of the relatively small sample size—it was tested on about 6,000 New Guineans who were exposed to the virus in 2015. Of those given the vaccine, none contracted the disease after 10 days of exposure. (The study did not count people who got sick within 10 days, as they were likely infected before they received the vaccine.)
While the efficacy is likely to decrease over time as more people are treated, scientists project that the vaccine will nonetheless be between 70 and 100 percent effective. In contrast, last year’s flu vaccine was 50 percent effective.
“Ebola left a devastating legacy in our country. We are proud that we have been able to contribute to developing a vaccine that will prevent other nations from enduring what we endured,” said Dr. KeÏta Sakoba, director of the national agency for health security in Guinea.
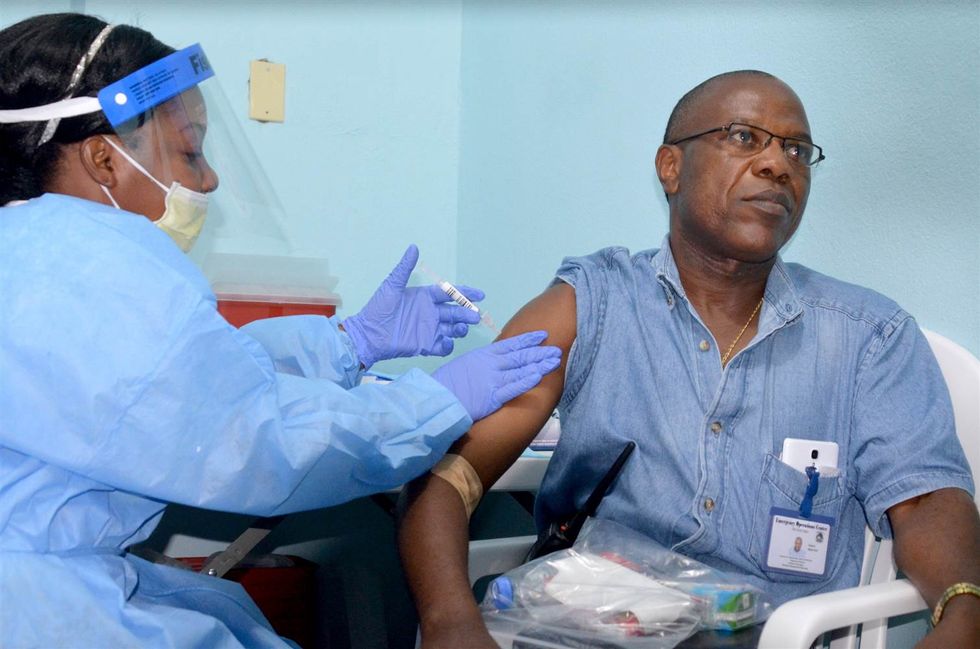
More studies need to be performed on the vaccine to answer open questions. For instance, said Dr. Anthony S. Fauci, director of the National Institute for Allergy and Infectious Diseases, “we don’t know how durable the vaccine is. If you give health care workers the vaccine, for example, how long would they be protected? That’s very important to learn.”
It also appears that the vaccine only works against one of the two most common strains of the virus.
“It’s certainly good news with regard to any new outbreak—and one will occur somewhere,” said Dr. Fauci. “But we will need to continue working on Ebola vaccines.”
The vaccine is expected to be approved sometime in 2018. In contrast, in typical cases, a new vaccine takes an average of ten years to become available. In the meantime, Merck, which is manufacturing the shot, has made 300,000 doses available in case of another outbreak.
“The world can’t afford the confusion and human disaster that came with the last epidemic,” said Marie-Paule Kieny, assistant director-general for health systems and innovation at the World Health Organization, and the study’s lead author.
“While these compelling results come too late for those who lost their lives during West Africa’s Ebola epidemic, they show that when the next outbreak hits, we will not be defenseless.”
 SECONDNEXUS
SECONDNEXUS percolately
percolately georgetakei
georgetakei comicsands
comicsands George's Reads
George's Reads