[DIGEST: Boston Globe, ABC News, National Geographic, The New York Times, The Smithsonian]
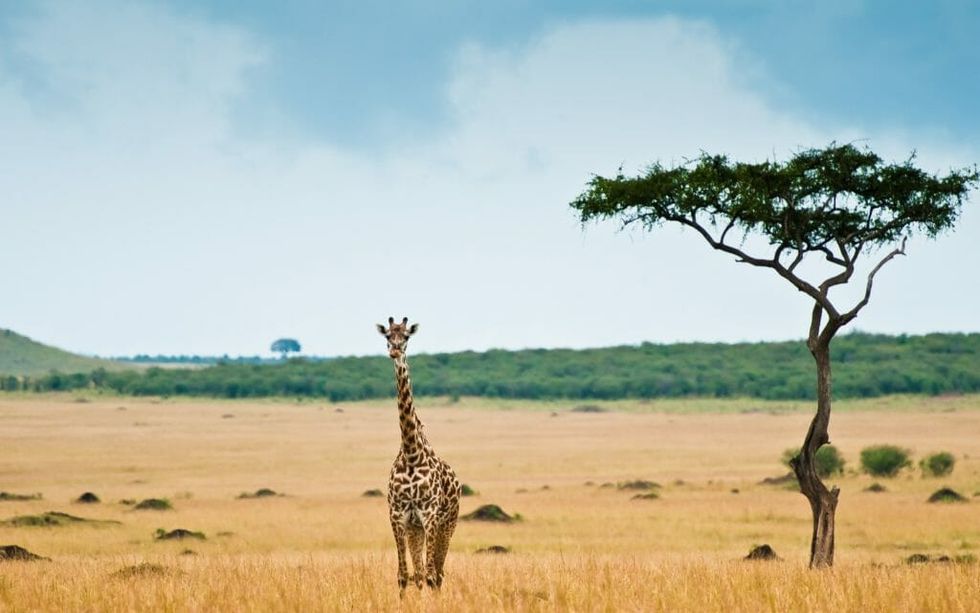
In an unexpected turn, giraffes have recently been added to the extinction watch list. The International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN), the organization that officially compiles the world’s endangered species list, held a biodiversity meeting in Mexico earlier this month and raised the threat level for 35 species while lowering it for seven species. For the first time, giraffes were stepped up from a species of “least concern” to “vulnerable,” meaning that giraffes could face extinction in the wild if steps aren't taken to minimize the threats that are dwindling the species’ numbers. Giraffes were the only mammal whose position shifted on that list this year.
Scientists attribute the giraffe’s addition to the red list to the decreased availability of habitat space, as areas of eastern and central Africa are being populated by people moving into giraffe territory. This combined with disease and poaching has led the giraffe population to shrink almost 40 percent over the last 30 years, a staggering drop from numbers upwards of 151,000 in 1985 compared to 97,562 in 2015, according to the IUCN.
Poaching of giraffes is another issue that often goes undiscussed. Hundreds of giraffes have been slaughtered every year solely for their long tails, which are considered a high status symbol in the Republic of the Congo. In addition, several different cultures will include giraffe tails as a valuable part of a girl’s wedding dowry.
Wild giraffes additionally can no longer be found in seven of their previously native countries – Burkina, Faso, Eritrea, Guinea, Malawi, Mauritania, Nigeria and Senegal, as reported by Noelle Kumpel of the Zoological Society of London.
While African animal conservation has primarily focused on elephants and the rhinoceros, both long-standing threatened species due to ivory poaching and habitat changes, giraffes were almost forgotten, with most assuming their populations were safe. Not until recently
have biologists admitted to doing a lackluster job evaluating the giraffe population and accurately determining their numbers.
"Everyone assumes giraffes are everywhere," said Julian Fennessy, co-director of the Giraffe Conservation Foundation, calling the giraffe decline a “silent extinction.”
The IUCN has received criticism for not accurately portraying the status of endangered and threatened species, something that should be at the core of the organization. Duke University conservation biologist Stuart Pimm says, “There's a strong tendency to think that familiar species (such as giraffes, chimps, etc.) must be OK because they are familiar and we see them in zoos… This is dangerous.”
The New York Times reports that of the nine giraffe subspecies, five of them are decreasing, with two increasing and one remaining stable. The smallest of the subspecies, the West African giraffe, has grown from a population of 50 in the 1990s to over 400 today with the aid of the Niger government creating and enforcing strict anti-poaching laws, as well as the benefits of ecotourism to generate money for continued conservation.
The largest of the subspecies, the Rothschild giraffe, recently increased by one, when the Oklahoma City Zoo and Botanical Garden welcomed a male giraffe calf in early December. The Rothschild giraffe is considered endangered with only 470 remaining in the wild in isolated parts of Kenya and Uganda.

There is still hope for these gentle giants and although giraffes have been placed on the red list, they are still a step away from being actually endangered. As an added bittersweet benefit, the alarming announcement is shifting the way biologists and conservationists are thinking about present and future protection for these animals.
 SECONDNEXUS
SECONDNEXUS percolately
percolately georgetakei
georgetakei comicsands
comicsands George's Reads
George's Reads