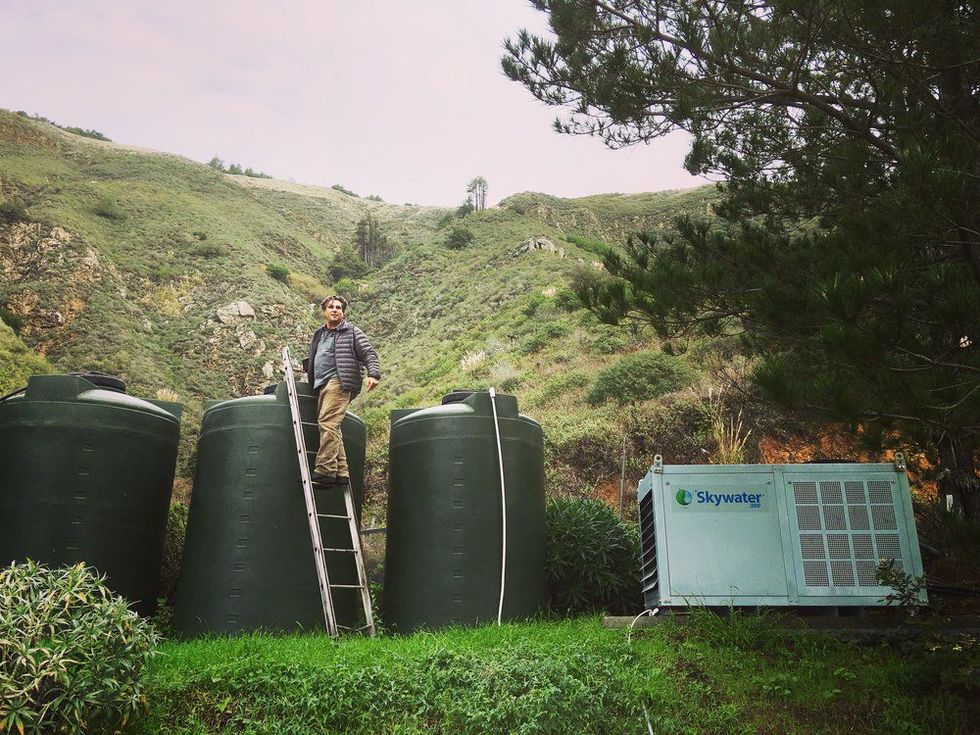
A California based team has designed a machine that can produce up to 300 gallons of fresh drinking water per day, simply by pulling it out of the air. The team won $1.5 million for their innovative creation.
[embed]
This machine can make gallons of fresh drinking water right out of thin air https://t.co/IN8QTNWahF— eric amtalla (@eric amtalla) 1540505319.0
Called Skywater, the machines were created by the Skysource/Skywater Alliance. The collective is a group of sustainability experts from Venice, California.
The Skywater machines are atmospheric water generators that condense water vapor from the atmosphere and turn it into drinking water. The machines are eco-friendly, running off of solar energy or the burning of biofuels. Housed in big metal boxes, the machines can be used for personal use, on farms, or in emergency relief efforts. Currently, nearly 800 million people are impacted by water scarcity.
[embed][/embed]
The $1.5 million prize (Water Abundance XPRIZE) was award by XPRIZE, a non-profit that runs competitions aimed at solving global problems, such as accessibility to clean drinking water. This particular contest lasted two years and was driven by the directive to solve the global water crisis through the development and accessibility of new technologies.
“We do a lot of first principles thinking at XPrize when we start designing these challenges,” says Zenia Tata, the Chief Impact Officer of XPrize.
Water is becoming increasingly scarce in numerous parts of the globe. The scarcity perpetuates difficulties surrounding agriculture, infrastructure in developing nations, and public health.
Tata realized that the amount of potential water that exists in the atmosphere far exceeds that needed by the human population.
“At any given time, it holds 12 quadrillion gallons–the number 12 with 19 zeros after it–a very, very, big number,” she says.
To put that number into perspective, the household needs for all 7 billion people on earth reaches approximately 350-400 billion gallons of water. This kind of technology has the potential to drastically reduce the issue of water scarcity.
"I've just been very, very interested in water ... but also the importance of fresh water to mankind. And in being in California, the issues are fast approaching crisis proportions," says David Hertz, one of the leaders of the Skysource/Skywater Alliance.
“It’s a carbon-negative technology. I think the future of technologies is going to be moving to this restorative, regenerative model that actually helps to repair the damage we’ve done. One could imagine these shipping containers being positioned in a state of readiness throughout the world to be able to respond to disasters for both energy and water,” he adds.
The Skywater machine is actually already in use in some areas. The team indicated that they will use the prize money to rapidly develop and distribute the machines worldwide. The team hopes to partner with nonprofits globally to achieve this feat.
 SECONDNEXUS
SECONDNEXUS percolately
percolately georgetakei
georgetakei comicsands
comicsands George's Reads
George's Reads