[DIGEST: HuffPo, ScienceAlert]
The very first modern case of a natural phenomenon called “river piracy” was recently detected in Canada.
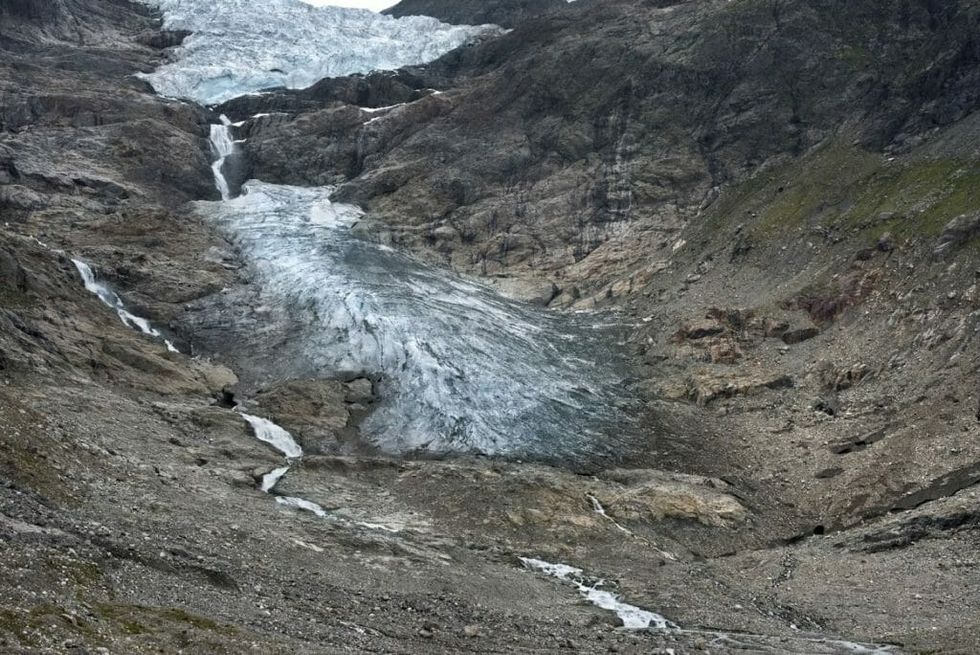
Between May 26 and May 29, 2016, the Slims River transformed from a rushing river at three meters deep and 480 meters (1,575 feet) wide, to a shallow, trickling creek that hardly covered scientists’ shoes at midstream — and it happened in a matter of just four days.
Researchers noticed this colossal change during a fieldwork expedition the following August. River gauges revealed to the team that this decrease in flow occurred due to a change in direction of water gushing from the Yukon’s massive Kaskawulsh Glacier. For 300-350 years, the glacier fed the Slims River, which would eventually flow into the Arctic’s Bering Sea; instead, the glacier’s watershed now flows into the Alsek River and ultimately into the Pacific Ocean.
River piracy, which is essentially the diversion of the headwaters of one stream into another, is capable of changing the routing of water and sediment. Eventually, this process alters a landscape drastically.

Typically, this process is studied over longer periods of time — and usually occurs over the course of thousands of years — but in the case of the Kaskawulsh Glacier, its retreat influenced and radically changed the regional drainage pattern in a brief period of time within the spring of 2016.
“Geologists have seen river piracy, but nobody to our knowledge has documented it happening in our lifetimes,” according to a geoscientist on the team of researchers, Dan Shugar, from the University of Washington Tacoma. He went on to describe the current Slims River as equivalent to “a long, skinny lake.”
This instance of river piracy was studied using a combination of hydrological measurements
and drone-generated digital elevation models, revealing that in late May 2016, meltwater rerouted from the Bering Sea to the Pacific Ocean.
The team of scientists studying the event at the Kaskawulsh Glacier determined that this happened due to post-industrial climate change, which can detrimentally affect ecosystems, sediment and carbon budgets. Unfortunately, there are downstream communities that may die off due to lack of sustained discharge.
“While one remote glacial river changing its course in the Yukon might not seem like a particularly big deal, glacier melt is a source of water for many people,” said geoscientist Rachel M. Headley, from the University of Wisconsin-Parkside, to The New York Times.
She added, “The sediments and nutrients that glacier rivers carry can influence onshore and offshore ecological environments, as well as agriculture.”
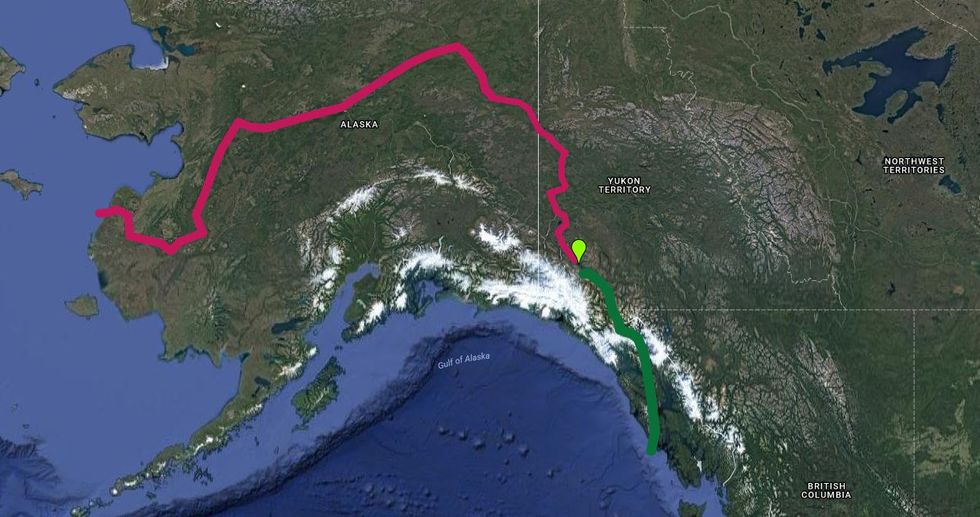
In this case, it is predicted that the now-diminished Slims River, as well as the Kaskawulsh River will adjust as a reaction to the adjusted watershed, and that Kaskawulsh watershed will reach into the newly-abandoned headwaters of the Slims River, and onward into the Kluane Lake drainage.
Though this is not the first time a river has dissipated due to river piracy, it is the first time in recorded history that this has ever occurred so quickly, and as a result of human-caused climate change.
Shugar’s team indicates that not all melting glaciers will result in events of river piracy, but the possibility is there.
“So far, a lot of the scientific work surrounding glaciers and climate change has been focused on sea-level rise,” Shugar explained in a press release. “Our study shows there may be other under-appreciated, unanticipated effects of glacial retreat.”
The disappearance of the Slims River is a sad reminder of how small rises in global temperature can threaten entire ecosystems.
 SECONDNEXUS
SECONDNEXUS percolately
percolately georgetakei
georgetakei comicsands
comicsands George's Reads
George's Reads